Russian Journal of Earth Sciences
Vol 1, No. 1, July 1998
Translated December 1998
Thermodynamics of deep geophysical media
V. L. Pankov
Schmidt United Institute of Physics of the Earth, Russian
Academy of Sciences, Bol'shaya Gruzinskaya ul. 10, Moscow,
123810 Russia
W. Ullmann, R. Heinrich, and D. Kracke
Geoscience Institute, Friedrich Schiller University of Jena,
Burweg 11, 07749 Jena, Germany
Contents
Abstract
Analysis of thermodynamic properties of geomaterials at
high pressures and temperatures existing in the Earth's
interior is presented. The presentation includes a summary on
the determination of equations of state based on measured
properties of minerals, as well as thermodynamic identities and
approximate relations between thermodynamic parameters of
the second, third, and in some instances, fourth orders. New
expressions were derived for the volume dependences of the
coefficient of thermal expansion, the Grüneisen
parameter, and
the Anderson-Grüneisen parameter. Attention
is given to the
preparation of the database on mineral properties. Several
geophysical estimates, including the lower-mantle properties,
were obtained. It was shown that the thermal expansivity
decreases 4-5 times along the "hot" mantle adiabat as the
pressure increases from 0 to 1.4 Mbar. Under the same
conditions, the heat capacity
CP drops about 10-15%. The
thermal pressure at
T > Q is linear in temperature, with
an accuracy of 1-3%. The parameter
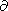 2KT/
2KT/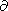 P
P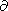 T at
P = 0 for
mantle minerals was estimated to be
(1-3)
T at
P = 0 for
mantle minerals was estimated to be
(1-3) 10-4 K
-1. The
acceptable ranges of other lower-mantle parameters are
dVT
= K
10-4 K
-1. The
acceptable ranges of other lower-mantle parameters are
dVT
= K - dT
- dT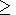 0.2,
q
0.2,
q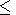 0.8,
g
0.8,
g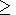 1.1,
dT
1.1,
dT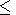 3-3.3, and
dS
3-3.3, and
dS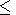 1.9-2.2. Deviations from
the Mie-Grüneisen equation of state are
discussed in
relation to the volume- and temperature-dependent Grüneisen
parameter.
1.9-2.2. Deviations from
the Mie-Grüneisen equation of state are
discussed in
relation to the volume- and temperature-dependent Grüneisen
parameter.
Load files for printing and local use.
This document was generated by TeXWeb
(Win32, v.1.0) on January 10, 1999.

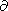 2KT/
2KT/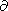 P
P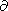 T at
P = 0 for
mantle minerals was estimated to be
(1-3)
T at
P = 0 for
mantle minerals was estimated to be
(1-3) 10-4 K
-1. The
acceptable ranges of other lower-mantle parameters are
dVT
= K
10-4 K
-1. The
acceptable ranges of other lower-mantle parameters are
dVT
= K - dT
- dT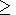 0.2,
q
0.2,
q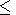 0.8,
g
0.8,
g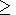 1.1,
dT
1.1,
dT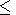 3-3.3, and
dS
3-3.3, and
dS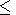 1.9-2.2. Deviations from
the Mie-Grüneisen equation of state are
discussed in
relation to the volume- and temperature-dependent Grüneisen
parameter.
1.9-2.2. Deviations from
the Mie-Grüneisen equation of state are
discussed in
relation to the volume- and temperature-dependent Grüneisen
parameter.
