A. A. Arzamastsev1, F. Bea2, V. N. Glaznev1, L. V. Arzamastseva1, and P. Montero2
1 Geological Institute, Kola Research Center, Russian Academy of Sciences,
Apatity,
Murmansk Oblast
2 University of Granada, Dept. of Mineralogy and Petrology, Fuentenueva
s/n, 18002, Granada, Spain
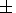 2700 sq. km. The
calculated composition of the magma that might have been melted from the mantle of
an intermediate composition revealed that a significant amount of incoherent elements
must have been added to the primary mantle material. It is shown with a high degree
of
certainty that the primitive magma was produced in the Kola Province because of the
low melting degree of the substrate (0.3-0.5%) whose composition answered to a
phlogopite (
2700 sq. km. The
calculated composition of the magma that might have been melted from the mantle of
an intermediate composition revealed that a significant amount of incoherent elements
must have been added to the primary mantle material. It is shown with a high degree
of
certainty that the primitive magma was produced in the Kola Province because of the
low melting degree of the substrate (0.3-0.5%) whose composition answered to a
phlogopite ( 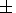 amphibole) bearing garnet lherzolite residing
at a depth of a garnet
mantle. The enrichment degree of this substrate was calculated to have been 3 times
higher than the mean contents of incompatible elements in the primitive mantle.
It is shown that the process of magma generation involved a significant portion
of the NE Fennoscandian lithosphere ca. 400 km across and 120 km in depth,
that is,
covered the entire depth of the mantle garnet lherzolite. This areal estimate agrees
with
the area of Paleozoic igneous rocks in the region. The estimated depth correlates
with
the PT conditions of the mantle xenoliths found in the dikes and breccia pipes of
the
region.
amphibole) bearing garnet lherzolite residing
at a depth of a garnet
mantle. The enrichment degree of this substrate was calculated to have been 3 times
higher than the mean contents of incompatible elements in the primitive mantle.
It is shown that the process of magma generation involved a significant portion
of the NE Fennoscandian lithosphere ca. 400 km across and 120 km in depth,
that is,
covered the entire depth of the mantle garnet lherzolite. This areal estimate agrees
with
the area of Paleozoic igneous rocks in the region. The estimated depth correlates
with
the PT conditions of the mantle xenoliths found in the dikes and breccia pipes of
the
region.
The research work done in the last decade furnished new proofs that the main factor responsible for continental magmatism in areas of ancient shields and their frames had been the reactivation of the upper mantle as result of a plume-lithosphere interaction and/or rifting [Baker et al., 1997; Bell and Simonetti, 1996; Kerr et al, 1995, 1996; Thompson and Gibson, 1991, 1994; Toyoda et al., 1994; White and McKenzie, 1989, 1995]. The results of deep seismic sounding combined with high-accuracy isotopic geochemical studies of mantle magmatic rocks and hypoxenoliths provided a basis for deriving models of magma generation in the mantle [Keen et al., 1994; McKenzie and O'Nions, 1991; Ryabchikov, 1998; White and McKenzie, 1995; Williamson et al., 1995]. Based on the latest experimental data, these models are good enough to determine the behavior of chemical elements for the partial melting of mantle rocks and to estimate the compositions and, in some cases, the volumes of the melting products [McKenzie and Bickle, 1988; Niu, 1997; Walter, 1998; Winter, 1995]. At the same time these approaches are liable for random assumptions because of the uncertainty of some data for magma generation in the mantle. This circumstance calls for deriving models based on alternative approaches to determining the volumes and compositions of mantle magmas.
This paper is an attempt to estimate the chemical composition and volume of the mantle, the melting of which resulted in the formation in Paleozoic time of the NE portion of the Baltic Shield in the Kola alkaline province and to evaluate the composition of the source melts. In contrast to the models mentioned above, we used a method of 3-D density modeling based on geophysical data [Glaznev et al., 1996].
The aims of this study were:
- to evaluate the volumes of the Paleozoic alkaline magmas in the region, including the calculation of the volumes of different types of rocks in the study area. The main results of this work, based on the study of the crust and mantle structure in the region and on the calculation of 3-D density models for all alkaline rock intrusions to a depth of 22.5 km, were reported earlier [Arzamastsev et al., 1998a; Arzamastsev et al., 2000a];
- to collect samples of plutonic, dike, and volcanic rocks for a geochemical study and perform high-precision determinations of trace elements concentrations using an ICP-MS method in the laboratory of the University of Granada following the procedure described in [Bea, 1996];
- to calculate the weighted average concentrations of trace elements in the rocks of the province, use the results to calculate the mean compositions of the source magmas, and compare the resulting compositions with the least differentiated rocks of the province;
- to carry out a petrologo-geochemical modeling including the calculation of the probable concentrations of trace elements in the source mantle melts (based on experimental data reported in literature), compare them with the calculated contents in the source Paleozoic magmas of the Kola Province, and calculate the potential volumes of the zone of Paleozoic magma generation for the given degrees of mantle rock melting.

|
| Figure 1 |
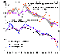
1. The province of study includes almost all products of the Paleozoic igneous activity including intrusions, dike swarms, and diatremes. The present-day level of the geological and geophysical knowledge of the Kola region [Mitrofanov et al., 1995] and of the adjacent areas of the Barents and White seas [Grachev, 2000a] suggests the minimum probability of discovering any new occurrences of Paleozoic igneous activity. This supposition is proved by the latest findings of alkaline rocks on the Barents Sea coast (Ivanovka Massif) [Rusanov et al., 1993], in the area of Lake Imandra (Niva intrusion) [Arzamastsev et al., 2000b], and in the Kandalaksha area (Kandaguba Massif) [Pilipyuk et al., 1998], whose contribution to the total volume of alkaline rocks in the province is not higher than 1%.
2. The level of the geological knowledge is high enough to reconstruct with a high degree of detail the internal structure of virtually all alkaline intrusions. Because most of the massifs were known to contain rare-metal ores, the area of all intrusions was covered by a large-scale geological survey, and the massifs were drilled to depths of 200-2000 m.
3. All products of Paleozoic igneous activity were emplaced during a relatively short time interval of 380-360 million years [Kramm et al., 1993]. This suggests that they originated during one strictly limited period of tectonomagmatic reactivation. This period was preceded by a long amagmatic period of the Baltic shield history, which lasted more than 1.3 billion years. No magmatic post-devonian events have been registered in the NE part of Fennoscandia.
4. The isotopic and geochemical characteristics of the Paleozoic plutonic and subvolcanic rocks of the province suggest the minimum contribution of crustal material in the origin of the alkaline rocks [Beard et al., 1998; Kramm and Kogarko, 1994; Zaitsev and Bell, 1995] and in the origin of their parental magmas as a result of the direct melting of the old mantle material depleted in the course of the Archean and Proterozoic crust formation [Arzamastsev et al., 1998b].
The above features place the Kola Province into the number of the most promising regions where the reconstruction of the initial composition of the mantle is permissible.
We calculated the volumes of the alkaline ultrabasic intrusions using the results of our 3-D density modelling based on geophysical data, which enabled us to determine the geological structure of the intrusions to a depth of 22 km. The essence of the regional density modelling of the Earth's crust under the Baltic shield and the technique of the 3-D density modelling of alkaline intrusions were discussed earlier [Arzamastsev et al., 2000a; The Structure of the Baltic Shield Lithosphere, 1993]. The interpretation of gravity data aimed at determining the structure of the central-type massifs consisted of two stages: first to calculate a regional density model for the crust and the gravity field it produced, and second to interpret the local gravity anomalies produced by density inhomogeneities in the upper crust.
Our calculation of a detailed density model for the upper crust was based on
the method and calculation technique offered by V. N. Strakhov
[Strakhov, 1990, 1999]
for solving a general inverse linear problem. In our practical use of this method
we introduced some additions to improve the convergence of the iteration solution
of
our 3-D inverse problem. To pick out local high-gradient anomalies, we used our own
version
of dispersion filtering, close in its sense to the known methods of adaptive filtering
[Nikitin, 1979].
The spacing of our grid for calculating a 3-D density
model was 2
 2 km in plan, and the vertical interval
was specified using a discrete
series of the grid nodes: 0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.5, 5.0, 7.0, 9.0, 11.0, and 14.0 km.
The accuracy
of solving the inverse gravity problem was chosen to be
2 km in plan, and the vertical interval
was specified using a discrete
series of the grid nodes: 0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.5, 5.0, 7.0, 9.0, 11.0, and 14.0 km.
The accuracy
of solving the inverse gravity problem was chosen to be
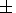 0.25 mgal. This accuracy
was sufficient for the accuracy of the density solution to be
0.25 mgal. This accuracy
was sufficient for the accuracy of the density solution to be
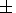 10 kg/m3. This
algorithm of the calculation and visualization of the results was used to write computer
programs to have the results of modelling in a graphic form.
10 kg/m3. This
algorithm of the calculation and visualization of the results was used to write computer
programs to have the results of modelling in a graphic form.
In our calculation of volumes we included all known occurrences of alkaline-ultrabasic and carbonatite magmatism (Kovdor, Turii Mys, Afrikanda, Sebl'yavr, Vuoriyarvi, and other intrusions), the huge alkaline rock complexes of Khibiny and Lovozero, and also volcanic rocks from the Kontozero caldera. In view of the fact that the volume of the Paleozoic alkaline dikes was hard to calculate, we assumed, using the swarms of alkaline lamprophyre dikes, known from the Kandalaksha River shore and from the Neblo Mt. area, their volume to be 10% of the total volume of the alkaline-ultrabasic intrusions. It is obvious that the error of determining the dike volume may be as high as 50% or even higher.

|
| Figure 2 |

|
| Figure 3 |
All alkaline-ultramafic intrusions were found to have a multiphase structure which reflects the successive intrusion of an alkaline ultramafics-foidolite-carbonatite series. It was believed earlier [Epshtein and Kaban'kov, 1984; Epshtein et al., 1972; Frolov, 1972; Kukharenko et al., 1965; Landa, 1976; Samoilov, 1977] that most of carbonatite intrusions had a zonal structure with carbonatite dominating in the top of the magma column, underlain by foidolite which is replaced at a deeper level by a zone of ultramafic rocks. Accordingly, the poorly eroded massif must show carbonatites, and the highly eroded ones, the rocks of the alkaline-ultramafic series. The results of our modeling confirmed this observation: the established relationship between the modern forms of the bodies and the depths to the bottoms of the magma chambers suggests that initially most of the Kola carbonatite intrusions had the form of a lenticular symmetrical stock with a distinct transition from the magma chamber to the feeding channel, the diameters of the latter being 1/5 to 1/3 of the maximum sizes of the intrusions [Arzamastsev et al., 2000a]. The apical part of this hypothetical intrusion seems to be represented in the Sokli Massif, where the carbonatites are associated with a large swarm of alkaline lamprophyre dikes, the fact typical of the poorly eroded intrusions. We used the Sebl'yavr and Kovdor intrusions, which preserved the large parts of their magma reservoirs, to reconstruct their sizes. We found that a ratio between the initial heights of the chambers and their diameters must have been 2:1, and the vertical lengths of the reservoirs, 15-20 km (Figure 3).
Using the data available on the deep structure of the intrusions, we calculated, for each of them, the volumes of their near-surface magma chambers, of their eroded parts, and of their feeding channels connecting the zone of magma generation and the shallow magma reservoir. The results of our calculations are presented in Table 1. We assumed that there had been no intermediate magma chambers in the crust or upper mantle. The circumstantial evidence of this is provided by isotopic data [Arzamastsev et al., 1998b; Kramm and Kogarko, 1994], suggesting an insignificant role of crustal contamination which would have been observed in the case of the long standing of mantle magma in crustal chambers.

|
| Figure 4 |
(1) the height of the magma chamber estimated from the results of the density modeling as a distance from the surface erosion level to the depth level of the transition to the feeding channel (h1 );
(2) the radius of the intrusion at the surface (R 1 ) found from the computed area of the massif. The latter and the outcrop areas of various rock types were computed from map data [Kukharenko et al., 1965, 1971];
(3) the radius of the magma chamber bottom (R2 ) at the level where it changes to a feeding channel estimated from the results of the density modelling. The maximum diameter of the chamber (R3 ) was calculated for intrusions of a lenticular form. In this case the volume was calculated as the sum of volumes of two truncated cones;
(4) Considering that the total volume of the magma chamber included its eroded portion, the volume of the latter was calculated using the radius of the intrusion near the surface (R1 ), the radius of the apical portion taken as 0.25R1, and the height h2 estimated as a difference between the height of a hypothetical carbonatite intrusion (15 km) [Arzamastsev et al., 2000a] and the height of the magma chamber h1;
(5) The volumes of the feeding channels were calculated using a formula for cylindrical bodies having a diameter measuring 0.25 of the bottom diameter of the intrusion and a height (h 3 ) equal to a distance from the bottom of the magma chamber to the zone of magma generation residing at a depth of ca. 55 km, as estimated in [Arzamastsev and Dalgren, 1993].
The volumes of the rocks making up the intrusions (dunite, pyroxenite, melilitholith, foidolite, and carbonatite) were estimated on the basis of their proportions at the eroded surface (Table 2) and of the results of the density modeling. For some intrusions (Sokli), the presence of silicate rocks in the uneroded portion of the massif was taken into account. It was assumed that the feeder was filled with the rock whose composition was similar to olivine melteigite porphyry. According to [Arzamastsev and Arzamastseva, 1990; Kochurova and Ivannikov, 1976; Kukharenko et al., 1971], the latter represents the average composition of the alkaline-ultramafic province.
With the adopted method of approximating the forms of the alkaline intrusions,
the errors of calculating their volumes were 10-15% for the magma chambers and
approximately 30% for the zone of the feeder and for the eroded portion. The
calculated total volume of all carbonatite intrusions of the province, including
the
volumes of their shallow chambers, feeders, and eroded portions, amounted roughly
to
4000
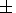 1000 km
3.
1000 km
3.

|
| Figure 5 |

|
| Figure 6 |
1. The southeastern, southern, and western contacts of the Lovozero Pluton are subvertical to a depth of 4 km in the zone of nepheline syenites and grow gentler beginning with the depths of 8-10 km (Figure 6). The northern and northwestern contacts are more gentle: the dips vary within 50-60o near the surface and within 30-40o at depths of 4-5 km. At greater depths the contact is subvertical to a depth of 9-10 km.
2. The Lovozero Pluton consists of two zones of different densities at a depth greater than 2 km (Figure 6). The southwestern zone is made up of rocks with densities of 2660-2750 kg/m3, these values being typical of nepheline syenite. A local negative density anomaly was recorded in the central part of the pluton in the Lake Sedyavr area. This anomaly marks a body of alkaline and analcime syenites with a density of 2580-2630 kg/m 3. This region seems to host a feeder for the nepheline syenite intrusion. The northeastern zone consists of rocks with a density higher than 2800 kg/m3. According to field geology and drilling data, the top of the zone is composed of the remnants of alkaline volcanic rocks of the Lovozero suite of Devonian age, and also of the alkaline-ultramafic rocks similar to those known from the Khibiny Massif [Arzamastsev et al., 1998a].
3. The conic-circular structure of the Khibiny Pluton persists within the depths accessible for observation, namely to a depth of 12.5 km. The eastern contact in the region of a carbonatite stock is subvertical to a depth of 3-4 km and tends to become suddenly gentler at a depth of 4-5 km. The western and southern contacts dip inward at an angle of 65-70o to a depth of 4 km. The position of the contact is as gentle as 30o in a depth interval of 4-6 km and becomes as steep as 50-60o below a depth of 7 km.
4. The results of our study suggest that the alkaline-ultramafic rocks are more abundant in the Khibiny Pluton than it was believed earlier [Galakhov, 1975]. The results of our density modeling show that boreholes reached merely the roof of a thick zone of alkaline ultramafics showing a positive density anomaly and extending along the entire northern sector of the massif (Figure 6). The holes drilled through the khibinites intersected thick zones composed of peridotite, pyroxenite, melilitolite, and ultrabasic foidolite xenoliths. The western sector of the pluton, which according to Snyatkova et al. [1986] is marked by a combination of gravity and magnetic anomalies, was found to include a large zone of alkaline ultramafics which extends as far as 15 km along a contact between the massive and the trachitoid khibinites. In contrast to the northern zone, the analysis of the structure of the southwestern part of what is known as an "ijolite-urtite arc'' showed the absence of positive density anomalies at low levels. This confirms the trend revealed by drilling that the ijolite-melteigite intrusion pinches out at a depth of ca. 3 km.
It follows from the above that the results of our 3-D density modelling were good enough to determine the structure of the Khibiny and Lovozero plutons to a depth of ca. 12 km, which is sufficient for estimating the total volumes of the magma reservoirs of these plutons and clarifying the volumetric relations of their rocks. Taking into account the circular configuration of these intrusions in plan, their total volume can be approximated as a sum of truncated cones, whose radii R1 -Rn and heights h1-hn are known (Figure 6). The calculations of the rock proportions in the total volume was performed on the basis of the density modelling within the areas outlined for the Khibiny and Lovozero plutons to the depths of 10.1 and 11.9 km, respectively. The results of our calculations are presented in Table 3. We assumed a priori that the radii of the feeding channels for these intrusions were 3 km for Khibiny and 1 km for Lovozero, these values being roughly 10% of the surface diameters of the intrusions. The channels have lengths equal to a distance between the bottom of the magma chamber and the zone of magma generation, which was inferred to reside at a depth of 55 km [Arzamastsev and Dalgren, 1993]. Taking into account the depth of erosion estimated by Virovlyanskii [1975] to be not more than a few kilometers, and also the numerous outliers of sedimentary and volcanic rocks that had formerly composed the roofs of the plutons, it can be assumed that the portion of the eroded rocks in the total volumes of the intrusions was approximately 10%.
Taking into account the approximated forms of the Khibiny and Lovozero
massifs, the errors of calculating their volumes are not higher than 10% for their
magma chambers, 30% for the feeders, and 40% for the eroded rocks. The calculated
total volumes of the Khibiny and Lovozero massifs, including the volumes of the
shallow chambers, feeders, and eroded rocks, were found to be 9100
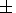 1400 km3 and 1600
1400 km3 and 1600
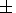 250 km3, respectively.
250 km3, respectively.
We calculated the average weighted concentrations of trace elements using the geochemical data obtained from analyzing the samples of the main varieties of Paleozoic igneous rocks in the Kola region. Our petrochemical data set included 1070 analyzes for the Khibiny Massif, 280 analyzes for the Lovozero Massif, 360, for the carbonatite intrusions, 230 analyzes for the volcanic rocks of the Lovozero and Kontozero suites, and 350 analyzes for the Paleozoic dikes and diatremes. The mean contents of trace elements were calculated using 116 analyzes of the representative samples of rocks collected in the above mentioned sites. Some of our chemical analyzes are presented in Tables 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11.
The procedure of calculating the average weighted compositions of the primary magmas consisted in computing first the mean contents of elements for each rock type and then the concentrations of elements, taking into account the rock volumes and densities. Apart from the rocks of the alkaline-ultramafic and phonolite series, calculations were made for the rocks of the Khibiny and Lovozero massifs (Table 12). Attempts to determine the compositions of the latter were made earlier, including high-precision techniques [Bussen and Sakharov, 1972; Gerasimovskii et al., 1966; Kukharenko et al., 1971]. The recent data on the age, geologic structure, and geochemistry of the Khibiny and Lovozero massifs suggest that they are composed of the rocks of two series: alkaline-ultramafic and phonolite ones [Arzamastsev et al., 1998a; Galakhov, 1988]. From this standpoint the mean composition of the Khibiny rocks calculated earlier [Kukharenko et al., 1971] does not give an idea of the composition of the primary magma of this unique massif. Moreover, our estimates of the mean compositions of the Khibiny and Lovozero rocks (Table 12) are different markedly from the earlier estimates [Kukharenko et al., 1971], because our calculations included a significant volume of the alkaline-ultramafic rocks from a depth of more than 2 km in the northern part of the Khibiny Massif and in the northeastern part of the Lovozero Massif. As a result, the chemical compositions of both massifs were displaced toward the higher contents of femic components and also of P, Cr, Ni, Co, Sc, and V.
To improve the reliability of our estimate of the average composition of the alkaline-ultrabasic magma, we compared our average weighted composition of the alkaline-ultramafic intrusions with the compositions of the contemporaneous rocks of the province representing the most primitive mantle magmas. The characteristics ascertaining the magmas to be most primitive and least differentiated mantle melts were (1) the magnesium number #mg > 68 found experimentally for the magnesium number of primary mantle melts [Eggler, 1989], (2) the relatively high contents of Ni and Cr, and (3) the mineralogical and petrographic evidence of the mantle origin of rocks, such as the presence of mantle xenoliths and/or of the xenocrysts of high-pressure phases (chrome diopside, Cr-bearing magnesian garnet, and chromite).
The most probable candidates, compositionally resembling the primary magmas of the Kola alkaline-ultramafic series, have been found in the Paleozoic volcanics and dikes, which were emplaced prior to and after the emplacement of the intrusions during a period of 405-360 Ma, respectively [Arzamastsev et al., 1998b; Kramm et al., 1993]. We distinguished the following groups of rocks.
1. The alkaline-ultramafic volcanic rocks of the Lovozero and Kontozero suites, as the earliest manifestations of the Paleozoic volcanic activity in the region. The alkaline picrites and ankaramites show #mg = 0.72-0.81, Ni = 160-520 ppm, Cr = 143-1100 ppm, and Co = 21-100 ppm. Some samples were found to contain chrome diopside xenocrysts.
2. The olivine and pyroxene melteigite porphyry, found in the satellites of large carbonatite intrusions and emplaced during the main stage of magmatic activity. In spite of the extensive development of these rocks in different areas of the Kola Peninsula (Turii Mys, Ivanovka, Ozernaya Varaka), the melteigite porphyry showed poor variations in the contents of petrogenic and trace elements (Tables 4 and 5). Except for the samples from Ozernaya Varaka, showing some indications of fractionation, the melteigite porphyry samples yielded #mg = 67-76, Ni = 140-610 ppm, and Cr = 310-820 ppm.
3. The olivine melanephelinite dikes and diatremes are spread over the entire territory of the Kola Peninsula, commonly concentrating in the frames of the alkaline intrusions. Geological data suggest that they were emplaced during the terminal phase of magmatic activity. Most of the dikes are poorly differentiated, as indicated by the presence of xenoliths and xenocrysts of mantle origin [Arzamastsev and Belyatskii, 1999], which could be preserved only under the condition of a relatively rapid rise of nephelinite magma from the zone of its generation. On this basis, the variety of olivine melanephelinite from the Namuaiv diatreme in the Khibiny Massif (Sample 1635/297.8) is comparable in terms of its Mg number and Ni and Cr contents with the most primitive magma.
Therefore we believe that the above mentioned three groups of rocks are most consistent with the primary magmas that were generated during a relatively short period of magmatic activity in northeastern Fennoscandia.
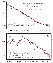
|
| Figure 7 |
In contrast to the rare earth elements, variations in the contents of other trace elements are more significant (Figure 7b), which stems, first, from the variations in the distribution of the accessory phases, such as apatite (P, Sr) and perovskite (Ti, Nb, Ta, Th), and, secondly, from the higher mobility of lithophile elements (Li, Rb). Nevertheless, the rocks of the initial, main, and terminal phases of magmatic activity show a regular, slow increase in the concentrations of most of incoherent elements in the rocks of the late phase. To sum up, our comparison shows that the average weighted contents of the majority of trace elements in the plutonic alkaline-ultramafic rocks, calculated with due allowance for geophysical data, agree with the values of the most primitive magmas of the alkaline-ultramafic series of the province, being most close to the contents in the olivine melteigite porphyry.
Proceeding from the fact that the products of the phonolite magma were found only in the Khibiny and Lovozero massifs, the basis for calculating the mean composition of the phonolite magma was, first, the analytical data for the samples of all types of agpaite syenites from these intrusions and, secondly, the results of our 3-D density modeling, which allowed us to calculate the average weighted contents of trace elements. The results are presented in Table 12. The phonolite magma was found to have a high agpaitic coefficient, (Na+K)/Al = 1.09, and high LILE and HFSE concentrations, higher than the average values for alkaline-ultramafic magmas. We could not compare our average weighted composition of phonolite magma with the compositions of phonolite from the dikes in the surroundings of the Kovdor, Vuoriyarvi, and Ivanovka massifs because of the great scatter of many trace element contents in the latter.
The data available for the concentration of petrogenic and trace elements in the rocks of the Kola Province are sufficient to estimate the composition of the mantle which was reactivated in Paleozoic time and served as a source of alkaline magma. The data available today for the composition of the mantle, the PT conditions of magma generation, the phase equilibria at high pressures, as well as for the distribution patterns of trace elements, are good enough to get correct results not only through modeling the conditions of komatiite magma generation [Herzberg and Zhang, 1997; Vrevskii, 2000; Walter, 1998; Wei et al., 1990], but also for the melting of moderately enriched mantle rocks [McKenzie and O'Nions, 1991; Niu and Hekinian, 1997; Pickering-Witter and Johnson, 2000; Walter et al., 1995].
It is known that the concentration of a trace element in magma CL is a function of the following variables: (1) the element concentration in the initial rock Co (wt.%); (2) the melting degree F (the amount of melt relative to the initial rock); (3) melting type (partial, fractional, etc.); (4) the number of mineral phases involved in the melting process; (5) the mineral-melt partition coefficient D. The initial substrate subject to melting can be primitive mantle [Hofmann, 1988], depleted mantle [McDonogh and Sun, 1995], and also metasomatized mantle enriched in incompatible elements. Because the contents of elements in depleted mantle and in primitive mantle were calculated using the composition of chondrite CI [Evensen et al., 1978] and were found to be 1.5 and 2.51, respectively, the results of modeling are applicable to both compositions, differing merely in the general amount of magma enrichment in incoherent elements. In all of the models calculated here we used the composition of primitive mantle as the initial mantle substrate (Tables 13 and 14). In our calculations we used the partition coefficients of olivine and orthopyroxene after [Beattie, 1994], of clinopyroxene after [Johnson, 1998], and of garnet after [Johnson, 1998; Prinzhofer and Allegre, 1985] (Tables 13 and 14). The values of the amphibole partition coefficients were used after [White, 1997].
The concentrations of elements in the products of partial melting CL were calculated using the standard formulas [Rollinson, 1993]:
where D0 is the bulk partition coefficient in the initial mantle rocks before melting, and P is the bulk partition coefficient calculated for the minerals producing the melt.
The composition of the restite CS was calculated using the formula
The models of the Rayleigh fractional melting were calculated by the formulas
for the derivates and the restite, respectively.
The PT conditions for the generation of nephelinite magmas in the Kola Province estimated using mantle xenoliths [Arzamastsev and Dalgren, 1993] show that alkaline-ultrabasic magmas might have been produced in the conditions of the mantle facies of spinel and garnet lherzolites. In the sections that follow we describe the calculations of the melting models:
(1) for normal primitive mantle (Tables 13 and 14) having the composition of spinel or garnet peridotite;
(2) for enriched mantle in which the concentrations of elements were 3 times as high as those in the primitive mantle; the versions here were for the melting of spinel and garnet peridotite, both containing amphibole and phlogopite.
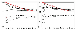
|
| Figure 8 |
The melting of mantle rocks with the composition of (Ol0.60 + Opx0.20 + Cpx0.08 + Grt0.12 ) [McKenzie and O'Nions, 1991] requires a higher pressure ( > 2.8 GPa), at which, in the melting interval of 0.1-15%, the compositions of the melts and complementary restites are controlled by the cotectic Ol0.05 + Opx0.05 + Cpx0.36 + Gr0.54. It should be noted that cotectic relationships are hard to determine at different PT conditions and can be estimated very roughly [Walter et al., 1995]. At the same time the composition of the cotectic is not essential because at low degrees of melting, the partitioning of trace elements between the melt and the restite takes place in accordance with their own D values.
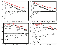
|
| Figure 9 |
 0%) is many
times lower than that observed in the magmas of the province. A specific feature
of the model discussed is a similarity between the composition of the restite
obtained for 1-per cent melting and the composition of depleted mantle after
[McKenzie and O'Nions, 1991].
0%) is many
times lower than that observed in the magmas of the province. A specific feature
of the model discussed is a similarity between the composition of the restite
obtained for 1-per cent melting and the composition of depleted mantle after
[McKenzie and O'Nions, 1991].
The models of the partial and fractional melting of trace elements (Figure 9, c and d) showed higher variations. This might have been caused by the higher mobility of some elements and by the less exact calculation of partition coefficients. Nevertheless, the data obtained for the majority of trace elements were similar to those for REE and showed the significantly higher Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf, and Y contents in the Kola primary melts, as compared to their threshold contents in the model melts with low melting degrees.
Inasmuch as the above models showed a low probability of getting melts enriched in incompatible elements, resembling the contents observed in the primary magmas of the Kola Province from the melts produced by the normal primitive mantle, this version was aimed to calculate the melting of mantle rocks, in which the contents of incompatible elements were taken to be n times higher than in primitive mantle.
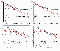
|
| Figure 10 |
We calculated a melting model for two compositions: Ol0.59 + Opx0.20 + Cpx0.08 + Grt0.08 + Phlog0.05 and Ol0.59 + Opx0.20 + Cpx0.08 + Grt0.08 + Phlog0.02 + Amph0.03. The existence of these mineral associations is controlled by the stability of phlogopite and/or amphibole in the presence of garnet and clinopyroxene in mantle conditions. K. Sato and E. Ito [1997] proved the stability of phlogopite in garnet harzburgite in the mantle underlying a craton at pressures growing as high as 5 GPa. On this basis they suggested the possibility of phlogopite formation as a secondary mineral produced by the reaction of garnet with the rising metasomatic fluid flow. It was supposed earlier [Dawson and Smith, 1982] that inasmuch as the stability of amphibole in the mantle is limited by a narrow pressure range, corresponding to a spinel facies depth, this mineral, in contrast to phlogopite, cannot be a receptacle of incoherent elements in deep zones of the mantle. However, Niida and Green [1999] showed that the stability of pargasite amphibole was controlled by the bulk content of Na2O+K2O in the mantle rocks: at T=1000oC, it is limited by pressure of 2.6 GPa and 0.33 wt.% Na2O+K2O, and grows higher at 2.9-3.0 GPa and 1.17 wt.% Na2O+K2O, thus extending into the garnet stability region. Moreover, Niida and Green [1999] discovered that the Na 2 O content in pargasite was also a function of pressure. Our calculations of the melts from the unenriched primitive mantle, quoted above, show that at low melting degrees ( F = 0.1-0.5%) the content of K2O alone rises as high as 0.5-1.1 wt.%. On the other hand, pargasite from the harzburgite xenoliths in the Khibiny Massif contains 2.91-3.10 wt.% Na2O. Therefore it can be assumed that under the PT conditions of magma generation in the Kola Province the mantle rocks might have contained not only phlogopite but also amphibole.

|
| Figure 11 |
|
| Figure 12 |
It appears that the existence of the enriched mantle substrate was related to the processes of a plume-lithosphere interaction, which produced extensive zones of metasomatized mantle. According to the results of studying mantle xenoliths, the mineral composition of mantle in zones of mantle metasomatism differs by the presence of amphibole, phlogopite, rutile, ilmenite, and apatite, in addition to olivine, orthopyroxene, clinopyroxene, spinel, and garnet [Haggerty, 1995; Konzett et al., 2000]. There is numerous evidence proving the existence of metasomatized mantle in regions of alkaline magmatism [Bailey, 1987; Wyllie, 1995; Yaxley et al., 1998], the Kola alkaline Province being one of them [Tolstikhin et al., 1999]. The direct proofs of the existence of the zones of mantle metasomatism in the region are the findings of spinel harzburgite xenoliths, containing pargasite and phlogopite, in a diatreme from the Khibiny Massif [Arzamastsev and Dalgren, 1993].
Our modeling of the behavior of trace elements during the melting of differently
enriched mantle rocks of different compositions showed that the generation of
primitive magmas in the Kola Province had been favored by the critically low melting
degrees of the rocks (0.3-0.5%) whose composition agreed with that of
phlogopite-bearing ( 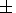 amphibole) lherzolite at a garnet mantle depth
( > 2.8 GPa). The resulting
melting degree (
amphibole) lherzolite at a garnet mantle depth
( > 2.8 GPa). The resulting
melting degree ( 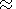 0.3%) agreed, for the given PT parameters,
with the calculations
modeling the melting of metasomatized mantle during a mantle plume-lithosphere interaction
[White and McKenzie, 1995].
0.3%) agreed, for the given PT parameters,
with the calculations
modeling the melting of metasomatized mantle during a mantle plume-lithosphere interaction
[White and McKenzie, 1995].
As a result of our calculations, we estimated the total volume of magma
generated during the time of Paleozoic tectonomagmatic reactivation. The computed
volume (15100
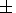 2700 km
3 ) includes the magmatic systems of the Khibiny
(9100
2700 km
3 ) includes the magmatic systems of the Khibiny
(9100
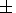 1400 km
3 ) and Lovozero (1600
1400 km
3 ) and Lovozero (1600
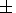 250 km
3 ) massifs, alkaline ultramafic
intrusions (4000
250 km
3 ) massifs, alkaline ultramafic
intrusions (4000
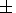 1000 km
3 ), and dikes (400
1000 km
3 ), and dikes (400
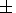 200 km
3 ). Experimental data
show that nephelinite melts of this type, enriched in incoherent elements, could
be
generated at the low degrees of mantle melting, not higher than 3-5%
[Edgar, 1987;
McKenzie, 1984].
One of the main factors controlling the minimum volume of mantle melt is
the ability of the melt to separate from the matrix, which mainly depends
on the content of volatiles
[Maaloe, 1998].
In the case of nephelinite melts, enriched significantly in H
2 O and CO
2 [Schiano et al., 1998;
Wyllie, 1995],
the volume of the mantle melt can be as small as 1%. Proceeding
from the calculated volume of the Paleozoic magma, the total volume of the partially
molten mantle rocks could be 3 to 5 million sq. km with the melting degrees of 0.3%
and 0.5%, respectively. It is obvious that these estimates of the volumes of the
magma
generation zone are minimal, because the calculation was made using the volumes of
the melted mantle rocks, whose manifestations are recorded at the level of erosion.
At
the same time, taking into account the unique features of geophysical anomalies
produced by alkaline intrusions, whose identification helps to trace the occurrences
of
alkaline magmatism to the depth of the lower crust base, we can suppose that our
calculations did not include the magmas that had not reached the ground surface but
had been conserved in the zone of the Devonian magma generation.
200 km
3 ). Experimental data
show that nephelinite melts of this type, enriched in incoherent elements, could
be
generated at the low degrees of mantle melting, not higher than 3-5%
[Edgar, 1987;
McKenzie, 1984].
One of the main factors controlling the minimum volume of mantle melt is
the ability of the melt to separate from the matrix, which mainly depends
on the content of volatiles
[Maaloe, 1998].
In the case of nephelinite melts, enriched significantly in H
2 O and CO
2 [Schiano et al., 1998;
Wyllie, 1995],
the volume of the mantle melt can be as small as 1%. Proceeding
from the calculated volume of the Paleozoic magma, the total volume of the partially
molten mantle rocks could be 3 to 5 million sq. km with the melting degrees of 0.3%
and 0.5%, respectively. It is obvious that these estimates of the volumes of the
magma
generation zone are minimal, because the calculation was made using the volumes of
the melted mantle rocks, whose manifestations are recorded at the level of erosion.
At
the same time, taking into account the unique features of geophysical anomalies
produced by alkaline intrusions, whose identification helps to trace the occurrences
of
alkaline magmatism to the depth of the lower crust base, we can suppose that our
calculations did not include the magmas that had not reached the ground surface but
had been conserved in the zone of the Devonian magma generation.

|
| Figure 13 |
These estimates agree with the data on the sizes of mantle plumes [Leitch et al., 1998] whose periods of igneous activity lasted 10 to 30 Ma. In particular, Grachev [2000] showed that the calculated size of the Kola Paleozoic plume was roughly similar to the products of plume magmatism in Greenland, Columbia, and Arabia.
The results of this study of the Paleozoic magmatism in the northeastern part of the Baltic Shield, based on geophysical and geochemical data and model calculations, can be summarized as follows.
1. The magma generated during the time of the Paleozoic tectonomagmatic
reactivation had a volume of 15,000
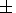 2700 km3. The total volume of mantle rocks
melted during a period of 380-360 million years might have been 3 to 5 million sq.
km, which corresponds to a region of the reactivated mantle as thick as 40 km
under
the entire Kola area involved in alkaline magmatic activity.
2700 km3. The total volume of mantle rocks
melted during a period of 380-360 million years might have been 3 to 5 million sq.
km, which corresponds to a region of the reactivated mantle as thick as 40 km
under
the entire Kola area involved in alkaline magmatic activity.
2. The calculated average weighted composition of the primary magmas in the Kola Province showed its similarity with the average composition of olivine melanephelinite and agreed with the compositions of the most primitive magmas found in the volcanic rocks and small intrusions of the region. The phonolite magma was found to have been enriched in Nb, Ta, Zr, and Hf, whereas no positive HFSE anomaly was found for the primitive alkaline-ultramafic magmas of the region.
3. The modelling of the trace element behavior during the melting of differently
enriched mantle rocks having different mineral compositions showed that (a) the
primary magmas of the Kola Province could not be derived from the primitive mantle
even at critically low melting degrees; (b) the generation of alkaline magma
at the PT
conditions of spinel stability is highly improbable; (c) the primitive magmas
could be
produced in the province as a result of the low melting degree of the rocks (0.3-0.5%),
under the conditions of a garnet mantle depth, whose enrichment was 3 times
higher than the average contents of incompatible elements in primitive mantle;
(d) also involved in melting were the mantle rocks with a composition of
phlogopite-bearing ( 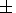 amphibole) garnet lherzolite.
amphibole) garnet lherzolite.
Arndt, N., K. Lehnert, and Y. Vasil'ev, Meimechites: Highly Magnesian Lithosphere-contaminated Alkaline Magmas from Deep Subcontinental Mantle, Lithos, 34, (1-3), 41-59, 1995.
Arndt, N., C. Chauvel, G. Czamanske, and V. Fedorenko, Two Mantle Sources, Two Plumbing Systems: Tholeiitic and Alkaline Magmatism of the Meymecha River Basin, Siberian Flood Volcanic Province, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 133, (3), 297-313, 1998.
Arzamastsev, A. A., and L. V. Arzamastseva, Undifferentiated Parental Magmas of the Alkaline Ultramafic Rocks of the Kola Region: Mineralogical and Geochemical Characteristics, in Mineralogy of the Alkaline Rocks and Associated Mineral Deposits of Karelia and Kola Peninsula, pp. 111-131, Petrozavodsk, 1990 (in Russian).
Arzamastsev, A. A., and B. V. Belyatskii, Evolution of the Mantle Source of the Khibiny Massif from the Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd Study of Mantle Xenoliths, Dokl. Ros. Akad. Nauk, 366, (3), 387-390, 1999.
Arzamastsev, A. A. and S. Dalgren, Mantle-Derived Mineral Associations in the Dike and Diatreme Rocks of the Baltic Shield, Geokhimiya, (8), 1132-1142, 1993.
Arzamastsev, A. A., L. V. Arzamastseva, V. N. Glaznev, and A. B. Raevskii, The Deep Structure and Composition of the Lower Units of the Khibiny and Lovozero Complexes, Kola Peninsula, Russia: A Petrological and Geophysical Model, Petrologiya, 6, (5), 478-496, 1998a.
Arzamastsev, A. A., L. V. Arzamastseva, and B. V. Belyatskii, Alkaline Volcanism of the Initial Phase of Paleozoic Tectonomagmatic Reactivation in the Northeast of Fennoscandia: Geochemistry and Petrologic Consequences, Petrologiya, 6, (3), 316-336, 1998b.
Arzamastsev, A. A., B. V. Belyatski, and L. V. Arzamastseva, Agpaitic Magmatism in the Northeastern Baltic Shield: A Case Study of the New Niva Intrusion, Kola Peninsula, Russia, Lithos, 51, (1/2), 27-46, 2000b.
Arzamastsev, A. A., V. N. Glaznev, L. V. Arzamastseva, and F. B. Raevsky, The Morphology and Internal Structure of the Kola Alkaline Intrusions, NE Fennoscandian Shield: 3D Density Modelling and Geological Implications, Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18, (2), 213-228, 2000a.
Bailey, D. K., Mantle Metasomatism - Perspective and Prospect, in Alkaline Igneous Rocks, J. G. Fitton and B. G. J. Upton, Eds., Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., issue 30, pp. 1-15, 1987.
Baker, J. A., M. A. Menzies, M. F. Thirlwall, and C. G. Macpherson, Petrogenesis of Quaternary Intraplate Volcanism, Sana'a, Yemen: Implications for Plume-Lithosphere Interaction and Polybaric Melt Hybridization, J. Petrol., 38, (10), 1359-1390, 1997.
Bea, F., Residence of REE, Y, Th, and U in Granites and Crustal Protoliths: Implications for the Chemistry of Crustal Melts, J. Petrol., 37, (3), 521-552, 1996.
Beard, A. D., H. Downes, E. Hegner, S. M. Sablukov, V. Vetrin, and K. Balogh, Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Devonian Ultramafic Minor Intrusions of the Southern Kola Peninsula, Russia: Implications for the Petrogenesis of Kimberlites and Melilitites, Contrib. Miner. Petrol., 130, 288-303, 1998.
Beattie P., Systematics and Energetics of Trace-Element Partitioning between Olivine and Silicate Melts: Implications for the Nature of Mineral-Melt Partitioning, Chemical Geology, 117, 57-71, 1994.
Bell, K., and F. Simonetti, Carbonatite Magmatism and Plume Activity: Implications from Nd, Pb, and Sr Isotope Systematics of Oldoinyo Lengai, J. Petrol., 37, (6), 1321-1339, 1996.
Bussen, I. V., and A. S. Sakharov, Petrology of the Lovosero Alkaline Massif, Nauka, Leningrad, 1972 (in Russian).
Dawson, J. B., and J. V. Smith, Upper-Mantle Amphiboles: A Review, Miner. Mag., 45, 35-46, 1982.
Edgar, A. D., The Genesis of Alkaline Magmas with Emphasis on Their Source Regions: Inferences from Experimental Studies, in Alkaline Igneous Rocks (J. G. Fitton and B. C. J. Upton, Eds.), Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., issue 30, pp. 29-53, 1987.
Eggler, D. H., Carbonatites, Primary Melts, and Mantle Dynamics, in Carbonatites: Genesis and Evolution, K. Bell (Ed.), pp. 561-579, (London: Unwin Hyman), 1989.
Epshtein, E. M., and V. Ya. Kaban'kov, The Depth of Formation and Metallic Minerals in Ultramafics, Ijolite and Carbonatite Massifs, Sov. Geol., (8), 85-98, 1984.
Epshtein, E. M., I. P. Pan'shin, V. M. Moralev, et al., Vertical Zoning in the Massifs of Ultrabasic Alkaline Rocks and Carbonatites, in Geology of Rare Earth Deposits, A. I. Ginsburg, Ed., issue 35, pp. 49-68, Nedra, Moscow, 1972 (in Russian).
Evensen, N. M., P. J. Hamilton, and R. K. O'Nions, Rare Earth Abundances in Chondritic Meteorites, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 42, (8), 1199-1212, 1978.
Frolov, A. A., Structural Conditions for the Formation of Ultrabasic Alkaline Rocks and Carbonatites, in Geology of Rare Earth Deposits, A. I. Ginzburg, Ed., issue 35, pp. 7-35, Nedra, Moscow, 1972 (in Russian).
Galakhov, A. V., Petrology of the Khibiny Alkaline Massif, Nauka, Leningrad, 1975 (in Russian).
Galakhov, A. V., Khibiny Alkaline Massif - a Complex Multisource Central-Type Intrusion, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 302, (3), 673-675, 1988.
Gerasimovskii, V. I., V. P. Volkov, L. N. Kogarko, A. I. Polyakov, T. V. Saprykina, and Yu. A. Balashov, Geochemistry of the Lovozero Alkaline Massif, Nauka, Moscow, 1966 (in Russian).
Glaznev, V. N., A. B. Raevsky, and G. B. Skopenko, A Three-Dimensional Integrated Density and Thermal Model of the Fennoscandian Lithosphere, Tectonophysics, 258, 15-33, 1996.
Grachev, A. F. (Ed.), Recent Tectonics, Geodynamics and Seismicity of Northern Eurasia, "Probel'', Moscow, 2000a (in Russian).
Grachev, A. F., Mantle Plumes and Problems of Geodynamics, Fizika Zemli, (4), 3-37, 2000b.
Haggerty, S. E., Upper Mantle Mineralogy, J. Geodynamics, 20, (4), 331-364, 1995.
Herzberg, C., and J. Zhang, Melting Experiments on Komatiite Analog Compositions at 5 GPa, Amer. Mineral., 82, (3/4), 354-368, 1997.
Hofmann, A. W., Chemical differentiation of the Earth: Relationships between Mantle, Continental crust and Oceanic Crust, Earth Planetary Science Lett., 90, (3), 297-314, 1988.
Irving, A. G., and F. A. Frey, Trace Element Abundances in Megacrysts and Their Host Basalts: Constraints on Partition Coefficients and Megacryst Genesis, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 48, 1201-1221, 1984.
Ivanikov, V. V., A. S. Rukhlov, and K. Bell, Magmatic Evolution of the Melilitite-Carbonatite-Nephelinite Dike Series of the Turii Peninsula (Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea, Russia), J. Petrol., 39, (11/12), 2043-2059, 1998.
Johnson, K. T. M., Experimental Determination of Partition Coefficients for Rare Earth and High-Field-Strength Elements between Clinopyroxene, Garnet, and Basaltic Melt at High Pressures, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 133, 60-68, 1998.
Keen, C.E., R. C. Courtney, M. C. Williamson, and S. A. Dehler, Decompression Melting at Rifted Margins: Comparison of Model Predictions with the Distribution of Igneous rocks on the Eastern Canadian Margin, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 121, 403-416, 1994.
Kennedy, C. S., and G. C. Kennedy, The Equilibrium Boundary between Graphite and Diamond, J. Geophys. Res., 81, 2467-2470, 1976.
Kerr, A. C., G. F. Marriner, N. T. Arndt, J. Tarney, A. Nivia, A. D. Saunders, and R. A. Cuncan, The Petrogenesis of Gorgona Komatiites, Picrites, and Basalts: New Field, Petrographic, and Geochemical Constraints, Lithos, 37, (2/3), 245-260, 1996.
Kerr, A. C., A. D. Saunders, J. Tarney, N. H. Berry, and V. L. Hards, Depleted Mantle-Plume Geochemical Signatures: No Paradox for Plume Theories, Geology, 23, (9), 843-847, 1995.
Kochurova, T. L., and V. V. Ivannikov, On the Nature of Olivine Melteigite Porphyry from the Turii Peninsula, Vestn. Leningr. Univ., 12, (2), 132-137, 1976.
Kogarko, L. N, Upper Mantle Heterogeneity and Alkaline Magmatism, Proc. 27th Int. Geol. Congress, vol. 11, section C. 11, Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry, pp. 159-164, Moscow, 1984 (in Russian).
Kogarko, L. N., V. A. Kononova, M. R. Orlova, and A. R. Woolley, Alkaline Rocks and Carbonatites of the World, Part 2., Former USSR, London: Chapman and Hall, 1995.
Konzett, J., R. A. Armstrong, and D. Gunther, Modal Metasomatism in the Kaapvaal Craton Lithosphere: Constraints on Timing and Genesis from U-Pb Zircon Dating of Metasomatized Peridotites and MARID-type Xenoliths, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 139, 704-719, 2000.
Kramm, U., L. N. Kogarko, V. A. Kononova, and H. Vartiainen, The Kola Alkaline Province of the CIS and Finland: Precise Rb-Sr Ages Define the 380-360 Age Range for All Magmatism, Lithos, 30, 33-44, 1993.
Kramm, U. and L. N. Kogarko, Nd and Sr Isotope Signatures of the Khibina and Lovozero Agpaitic Centers, Kola Alkaline Province, Russia, Lithos, 32, 225-242, 1994.
Kukharenko, A. A., A. G. Bulakh, G. A. Il'inskii, N. F. Shinkarev, and M. P. Orlova, Metallogeny of Alkaline Rocks in the East of the Baltic Shield, Trudy Leningr. Ob-va Estestvoispyt., 72, (2), p. 280, 1971.
Kukharenko, A. A., M. P. Orlova, A. G. Bulakh, E. A. Bagdasarov, O. M. Rimskaya-Korsakova, E. I. Nefedov, G. A. Il'inskii, A. S. Sergeev, and N. B. Abakumova, The Caledonian Complex of Ultrabasic Alkaline Rocks and Carbonatites of the Kola Peninsula and Karelia, Nedra, Moscow, 1965 (in Russian).
Kukkonen, I. T., and P. Peltonen, Xenolith-Controlled Geotherm for the Central Fennoscandian Shield: Implications for Lithosphere-Asthenosphere Relations, Tectonophysics, 304, (4), 301-315, 1999.
Landa, E. A., Petrographic Types and Vertical Zoning of Ultrabasic Alkaline Rock Massifs, Geologiya i Geofizika, (10), 65-72, 1976.
Le Bas, M. J., Nephelinites and Carbonatites, in Alkaline Igneous Rocks, Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., Fitton, J. G. and Upton, B. G. J. (Eds.), issue 30, pp. 53-83, 1987.
Leitch, A. M., G. F. Davies, and W. Wells, A Plume Head Melting under a Rifting Margin, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 161, 161-167, 1998.
Maaloe, S., Melt Dynamics od a Layered Mantle Plume Source, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 133, 83-95, 1998.
McDonough, W. F., and S. S. Sun, The Composition of the Earth, Chem. Geol., 120, 223-253, 1995.
McKenzie, D., The Generation and Compaction of Partially Molten Rock, J. Petrol., 25, 713-765, 1984.
McKenzie, D., and M. J. Bickle, The Volume and Composition of Melt Generated by Extension of the Lithosphere, J. Petrol., 29, 625-679, 1988.
McKenzie, D., and R. K. O'Nions, Partial Melt Distributions from Inversion of Rare-Earth Element Concentrations, J. Petrol., 32, (5), 1021-1091, 1991.
Mitrofanov, F. P., V. I. Pozhilenko, V. F. Smolkin, A. A. Arzamastsev, V. Ya. Yevzerov, V. V. Lyubtsov, S. V. Nikolaeva, and Zh. A. Fedotov, Geology of the Kola Peninsula (Baltic Shield), 144 p., Apatity, 1995.
Niida, K., and D. H. Green, Stability and Chemical Composition of Pargasitic Amphibole in MORB Pyrolite under Upper Mantle Conditions, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 135, 18-40, 1999.
Nikitin, A. A., Statistical Method of Locating Geophysical Anomalies, Nedra, Moscow, 1979 (in Russian).
Niu, Y., Mantle Melting and Melt Extraction Processes beneath Ocean Ridges: Evidence from Abyssal Peridotites, J.Petrol., 38, (6), 1047-1074, 1997.
Niu, Y., and R. Hekinian, Basaltic Liquids and Hartzburgitic Residues in the Garrett Transform: A Case History at Fast-Spreading Ridges, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 146, 243-258, 1997.
Pickering-Witter, J., and A. D. Johnston, The Effects of Variable Bulk Composition on the Melting Systematics of Fertile Peridotitic Assemblages, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 140, (1), 190-211, 2000.
Pilipyuk, A. N., V. V. Ivanikov, and O. E. Goliyanova, Geochemistry and Genesis of Kandaguba Carbonatites (Kola Peninsula): Problems of the Origin of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks, Abstracts of papers, Intern. Conf. 100th Anniversary of N. A. Eliseev, pp. 120-121, Saint Petersburg, 1998.
Prinzhofer, A., and C. J. Allegre, Residual Peridotites and Mechanism of Partial Melting, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 74, (2/3), 251-265, 1985.
Robinson, J. A. C., and B. J. Wood, The Depth of the Spinel to Garbet Transition at the Peridotite Solidus, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 164, 277-284, 1998.
Rock, N. M. S., The Nature and Origin of Lamprophyres: An Overview in Fitton, J. G. and Upton, B. G. J. (Eds.), Alkaline Igneous rocks, Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., issue 30, pp. 191-226, 1987.
Rollinson, H. R., Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation, Longman Sci. and Tech., Co-published Wiley and Sons, New York, 1993.
Rukhlov, A. S., Primary Alkaline Melts and Igneous Series of the Kandalaksha Graben, Russia, in Mineral Deposits, H. Papunen (Ed.), pp. 785-787, Balkema, Rotterdam, 1997.
Rusanov, M. S., A. A. Arzamastsev, and V. I. Khmelinskii, A New Volcanoplutonic Complex in the Kola Alkaline Province, Otechestv. Geol., (11), 35-43, 1993.
Ryabchikov, I. D., Geochemical Modelling of Magma Generation in Passive and Active Mantle Plumes in Challenges to Chemical Geology, Novak, M. and Rosenbaum, J. (Eds.), Prague: Czech Geological Survey, pp. 103-120, 1998.
Salters, V. J. M., and J. Longhi, Trace Element Partitioning during the Initial Stages of Melting beneath Mid-Ocean Ridges, Earth and Planet. Sci. Lett., 166, 15-30, 1999.
Samoilov, V. S., Carbonatites: Facies and Origin, Nauka, Moscow, 1977 (in Russian).
Sato, K., and E. Ito, Phase Relations of Natural Phlogopite with and without Enstatite up to 8 GPa: Implications for Mantle Metasomatism, Earth and Planet. Sci. Lett., 146, (3/4), 511-526, 1997.
Schiano, P., B. Bourdon, R. Clocchiatti, D. Massare, M. E. Varela, and Y. Bottinga, Low-degree Partial Melting Trends Recorded in Upper Mantle Minerals, Earth and Planet. Sci. Lett., 160, 537-550, 1998.
Snyatkova, O. L., N. I. Pronyagin, T. M. Markitakhina, and A. S. Evstafiev, New Data on the Structural Position of the Urtite-Ijolite-Melteigite Complex in the Nepheline Syenites of the Khibiby Massif, in Nonmetallic Mineral Deposits of the Kola Peninsula, pp. 11-17, Izd. Kolskogo Filiala Akad. Nauk SSSR, Apatity, 1986 (in Russian).
Strakhov, V. N., A Theory of Linear Inverse Gravity Problems, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 311, (5), 1093-1096, 1990.
Strakhov, V. N., Geophysics and Mathematics: Methods of Mathematical Geophysics, United Institute of Physics of the Earth, Russ. Acad. Sci., Moscow, 1999 (in Russian).
Ternovoi, V. I., Carbonatite Massifs and Their Mineral Deposits, University Press, Leningrad, 1977 (in Russian).
The Structure of the Baltic Shield Lithosphere, Sharov N. V., Ed., VINITI, Moscow, 1993 (in Russian).
Thompson, R. N., and S. A. Gibson, Subcontinental Mantle Plumes, Hotspots, and Pre-existing Thinspots, J. Geol. Soc. London, 148, 973-977, 1991.
Thompson, R. N., and S. A. Gibson, Magmatic Expression of Lithospheric Thinning across Continental Rifts, Tectonophysics, 233, (1/2), 41-68, 1994.
Tolstikhin, I. N., I. L. Kamenetsky, V. A. Nivin, V. R. Vetrin, E. G. Balaganskaya, S. V. Ikorsky, M. A. Gannibal, Yu. M. Kirnarsky, B. Marty, D. Weiss, A. Verhulst, and D. Demaiffe, Low Mantle Plume Component in 370 Ma old Kola Ultrabasic-Alkaline-Carbonatite Complexes: Evidence from Rare Gas Isotopes and Related Trace Elements, Russian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1, (2), 125-143, 1999.
Toyoda, K., N. Horiuchi, and M. Tokonami, Dupal Anomaly of Brazilian Carbonatites: Geochemical Correlations with Hotspots in the South Atlantic and Implications for the Mantle Source, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 126, (4), 315-332, 1994.
Virovlyanskii, G. M., Effect of the Emplacement Depth and Erosion of the Khibiny and Lovosero Massifs on Their Agpaite Content, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Geologiya, (11), 90-98, 1975.
Vrevskii, A.B., Komatiite Petrology, the Isotopic and Geochemical Evolution of the Upper Mantle and the Geodynamics of Greenstone Belts, Doctoral (Geol.) Dissertation, p. 316, Saint Petersburg State University, 2000.
Walter, M. J., Melting of Garnet Peridotite and the Origin of Komatiite and Depleted Lithosphere, Journal of Petrology, 39, (1), 29-60, 1998.
Walter, M. J., T. W. Sisson, and D. C. Presnall, A Mass Proportion Method for Calculating Melting Reactions and Application to Melting of Model Upper Mantle Lherzolite, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 135, (1-4), 77-90, 1995.
Wei, K., R. Tronnes, and C. M. Scarfe, Phase Relations of Aluminium-Undepleted and Aluminium-Depleted Komatiites at Pressures of 4-12 GPa, J. Geophys. Res., 95, 15,817-15,827, 1990.
White, R. S., and D. McKenzie, Magmatism at Rift Zones: The Generation of Volcanic Continental Margins and Flood Basalts, J. Geophys. Res., 94, (B6), 7685-7729, 1989.
White, R. S., and D. McKenzie, Mantle Plumes and Flood Basalts, J. Geophys. Res., 100, (B9), 17,543-17,586, 1995.
White, W. M., Geochemistry, WWW Publication: http://www.geo.cornell.edu/geology/classes/chapters.html, 554 p., 1997.
Williamson, M.-C., R. C. Courtney, C. E. Kee, and S. A. Dehler, The volume and Rare Earth Concentrations of Magmas Generated during the Finite Stretching of the Lithosphere, Journal of Petrology, 36, (5), 1433-1454, 1995.
Winther, K. T., A Model for Estimating the Composition of Partial Melts, Mineral. and Petrol., 53, (1-3), 189-196, 1995.
Wyllie, P. J., Experimental Petrology of Upper Mantle Materials, Processes and Products, J. Geodynamics, 20, (4), 429-468, 1995.
Yaxley, G. M., D. H. Green, and V. Kamenetsky, Carbonatite Metasomatism in the Southeastern Australian lithosphere, Journal of Petrology, 39, (11/12), 1917-1930, 1998.
Zaitsev, A. N., and K. Bell, Sr and Nd Isotope Data of Apatite, Calcite, and Dolomite as Indicators of the Source and the Relationships of Phoscorites and Carbonatites from the Kovdor Massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 121, 324-335, 1995.