Russian Journal of Earth Sciences
Vol. 4, No. 3, June 2002
Gamma ray spectrometry of rocks from a volcanic sequence
penetrated by the SG-1 borehole and the radiogenic contribution
to the total heat flow
Ch. S. Aliev, T. A. Zolotovitskaya and T. A. Ismailzade
Abstract
Results derived from gamma-ray spectrometry studies of volcanic rocks
in a depth interval of 3540-8150 m are presented. The rocks are shown to have
low
concentrations of radioactive elements, which is consistent with the clarke of basic
igneous rocks close to calc-alkalic series of present island-arc systems. Potassium
is present
in all rocks of the volcanic sequence, whereas uranium and thorium are absent in
some of its beds. Maximum U and Th concentrations are 4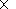 10-4%
and 6
10-4%
and 6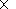 10-4%, respectively.
The Mesozoic sequence was subdivided into
seven groups in accordance with associations of radioactive elements. The distribution
of radioactive elements and their associations along the SG-1 section can be accepted
as criteria for the differentiation of the volcanic sequence. Estimates of the radiogenic
heat generation calculated for rocks of the volcanic sequence point to a considerable
contribution of the radiogenic heat to the total heat flow.
No proportionality exists between the radiogenic heat generation in the crust
and measured heat flow.
10-4%, respectively.
The Mesozoic sequence was subdivided into
seven groups in accordance with associations of radioactive elements. The distribution
of radioactive elements and their associations along the SG-1 section can be accepted
as criteria for the differentiation of the volcanic sequence. Estimates of the radiogenic
heat generation calculated for rocks of the volcanic sequence point to a considerable
contribution of the radiogenic heat to the total heat flow.
No proportionality exists between the radiogenic heat generation in the crust
and measured heat flow.
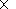 10-4%
and 6
10-4%
and 6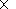 10-4%, respectively.
The Mesozoic sequence was subdivided into
seven groups in accordance with associations of radioactive elements. The distribution
of radioactive elements and their associations along the SG-1 section can be accepted
as criteria for the differentiation of the volcanic sequence. Estimates of the radiogenic
heat generation calculated for rocks of the volcanic sequence point to a considerable
contribution of the radiogenic heat to the total heat flow.
No proportionality exists between the radiogenic heat generation in the crust
and measured heat flow.
10-4%, respectively.
The Mesozoic sequence was subdivided into
seven groups in accordance with associations of radioactive elements. The distribution
of radioactive elements and their associations along the SG-1 section can be accepted
as criteria for the differentiation of the volcanic sequence. Estimates of the radiogenic
heat generation calculated for rocks of the volcanic sequence point to a considerable
contribution of the radiogenic heat to the total heat flow.
No proportionality exists between the radiogenic heat generation in the crust
and measured heat flow.