RUSSIAN JOURNAL OF EARTH SCIENCES, VOL. 20, ES6014, doi:10.2205/2020ES000752, 2020
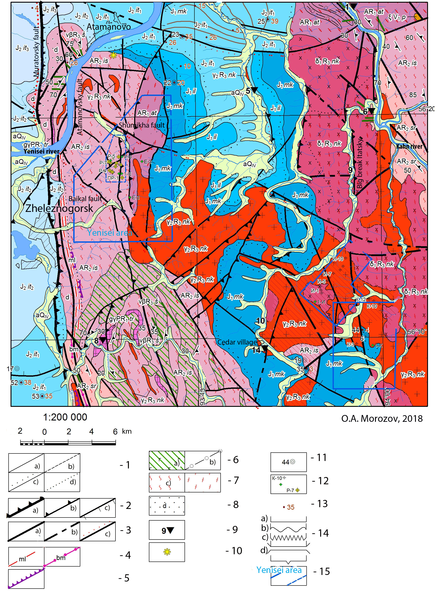
Figure 1. Geological map of the Nizne-Kansk massif. 1 - boundaries: established (a), assumed (b), unconformity (c), dropping (d); 2 - reverse faults: major (a), minor (b), faults (c); 3 - breaking faults: unidentified (a), alleged (b), activated (c); 4 - mylonites (a), blastomylonites (c); 5 - tectonic terrain ledges; 6 - amphibolites (a), shales (b); 7 - migmatites (a), granitoids (b); 8 - diaftorites; 9 - outcrops; 10 - places of permafrost; 11 - holes; 12 - wells in area HLRW; 13 - thickness of the Quaternary layer; 14 - the relationship of layers: consonant (a), unconformable (b), angular unconformity (c), tectonic (d), intrusive (e); 15 - boundaries of areas for HLRW.
Citation: Agayan S. M., V. N. Tatarinov, A. D. Gvishiani, Sh. R. Bogoutdinov, I. O. Belov (2020),
Copyright 2020 by the Geophysical Center RAS.
Generated from LaTeX source by ELXfinal, v.2.0 software package.

